Get AHSEC Class 12 Biology Chapter: 7 Human Health and Diseases Important Questions Answers 2025. In this post we have Prepared for you Assam Board Biology Chapter: 7 Solution as Per AHSEC Latest Syllabus and exam patterns.
AHSEC Class 12 Biology Chapter: 7 Human Health and Diseases Solution Can be a great resource for your exam preparation. Use this chapter’s Notes/Solution as a guideline or reference.
An Overview of AHSEC Class 12 Biology Notes for 2025
| Name of Board | AHSEC |
| Class: | Assam Board Class 12 |
| Subject: | AHSEC Class 12 Biology |
| Number of Chapter: | 07 |
| Chapter Name | Human Heath and Diseases |
| Content Type: | Text, Images and PDF Format |
| Academic Year: | 2024-25 |
| Medium: | English |
| Available Solution Link: | AHSEC Class Biology Notes |
AHSEC Class 12th Biology Chapter: 7 Human Health and Diseases
SPECIAL QUESTION : (1 MARK)
1. Disease causing organism.
Ans. Pathogens
2. Causative agent of malignant malaria
Ans. Plasmodium falciparum.
3. The yellowish fluid secreted by mother during initial days of lactation.
Ans. Colostrum.
4. A group of symptoms of a disease.
Ans. Syndrome.
5. The agents which cause cancer
Ans. Carcinogens.
[A] FILL IN THE BLANKS :
1. Blood circulation in human body was discovered by_____.
Ans. William Harvey
2. Typhoid fever could beconfirmed by ______test.
Ans. Widal
3. Common cold is a______disease.
Ans. Viral
4. Filariasis is Caused by_______.
Ans. Wuchereria
5. AIDS can be diagnosed by______test
Ans. ELISA
6. Heroin is obtained by ______of morphine.
Ans. Acetylation
7. Cocaine interfere with the transport of the neuro- transmitter_______.
Ans. Dopamine
8. The lymphoid tissue located within the lining of the respiratory, digestive and urinogenital tracts is called_______
Ans. MALT (Mucosal Associated lymphoid tissue)
[B] TRUE OR FALSE :
1. Genetic diseases are inborn.
Ans. True
2. AIDS is a non-infectious disease.
Ans. True
3. Typhoid is caused by virus.
Ans. False
4. In common cold lung is infected.
Ans. False
5. A healthy person aquires ascariasis infection through blood transfusion.
Ans. False
6. The genome of HIV is RNA.
Ans. True
7. Oncogenic viruses are cancer causing viruses.
Ans. True
8. The chronic use of durgs and alcohol damage nervous system and liver.
Ans: True
[C] VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
(1 MARK)
1. Define health.
Ans: Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well being
2. How can you maintain good health?
Ans: Good health, can be maintained by balanced diet, personal hygiene and regular exercise.
3. What is disease?
Ans: Disease is a condition when the functioning of one or more organs or systems of the body is adversely affected, characterised by various signs and symptoms.
4. Write the biological name of the bacterium causing typhoid.
Ans: Salmonella typhi.
5. Why Mary Mallon was nicknamed as typhoid Mary?
Ans: Mary Mallon was a cook by profession and was a typhoid carrier who continued to spread Typhoid for several years through the food she prepared. So she was nicknamed as Typhoid Mary.
6. How a healthy person is infected by typhoid fever?
Ans: A healthy person is infected by typhoid when the pathogens generally enter the small intestine through contaminated food and water and migrate to other organs through blood.
7. Name the bacteria which cause pneumonia in man.
Ans: Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae.
8. Which type of malaria is fatal to man?
Ans: Malignant malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
9. Why ringworm infections are prevalent in groin and other skin folds?
Ans: Because heat and moisture help the fungi to grow, so they are prevalent in groin and other skin folds.
10. In treating snake bite which type of immunisation is performed?
Ans: Passive immunisation.
11. What type of immunity is responsible for graft rejection?
Ans: Cell mediated immunity (CMI).
12. What is the causative virus of AIDS? To which group of virus it belongs to?
Ans: Human Immuno Deficiency Virus (HIV) is the causative agent of AIDS. It belongs to retrovirus group.
13. What is cancer?
Ans: Cancer is a disease characterised by breaking down of regulatory mechanisms of normal cells, uncontrolled division of cells and the movement of proliferating cells to other parts of the body.
14. Define contact inhibition.
Ans: Contact inhibition is a property of the normal cells by virtue of which contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth.
15. Name the drugs which are commonly abused.
Ans: Opioids, cannabinoids and coca alkaloids.
16. State the affects of heroin.
Ans: Heroin is a depressant and slows down body functions.
17. Name the plant from which morphine is extracted.
Ans: Papaver somniferum.
18. What are connabinoids?
Ans: Cannabinoids are a group of chemicals which interact with cannabinoid receptors present principally in the brain.
19. What is benign tumour?
Ans. Benign tumour remain confined to their original location and do not spread to other parts of the body and cause little damage.
20. Write the full form of ELISA.
Ans. Enzyme Linked Immune sorbent Assay.
21. Name the property of normal cells by which uncontrolled growth of cell is inhibited.
Ans. Contact inhibition.
[D] Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. What are the 2 basic groups of diseases? Give one example of each group.
Ans: Diseases are grouped into
(i) Infectious diseases: These are easily transmitted from one infected person to the other. They are caused due to extrinsic factors. e.g. AIDS.
(ii) Non-infectious diseases: They are not transmitted from one person to the other. they are caused due to extrinsive and intrinsic factors. e.g. Cancer.
2. Write a note on pathogens.
Ans: A wide range of organisms belonging to bacteira, viruses, fungi, protozoans, helminths etc. could cause diseases in man and are called pathogens. All parasites are pathogens as they cause harm to the host by living in (or on) them. The pathogens can enter our body by various means, multiply and interfere with normal vital activities, resulting in morphological and functional damage. Pathogens for their survival have to adapt to life within the environment of the host.
3. State the symptoms of typhoid.
Ans: (i) Sustained high fever (39 to 40°C)
(ii) Weakness
(iii) Stomach pain
(iv) Constipation
(v) Headache
(vi) Loss of appetite.
4. Name 4 bacterial diseases of man.
Ans: Typhoid, pneumonia, diptheria, plague.
5. How common cold disease spread from one to another person?
Ans: Droplets resulting from cough or sneezes of an infected person are either inhaled directly or transmitted through contaminated objects such as pens, books, cups, doorknobs, computer keyboard or mouse etc, and cause infection in a healthy person.
6. State the symptoms of common cold.
Ans: (i) Nasal congestion and discharge
(ii) Sore throat
(iy) hoarseness
(v) Cough
(v) headache
(vi) Tiredness
7. ‘Malarial parasite is digenetic’. Explain.
Ans: Plasmodium requires two hosts to complete its life cycle- human and mosquito. The infected female Anopheles mosquito transfers the sporozoites to the human body by biting which reaches the liver cells and multiply. This is followed by their attack on RBCs resulting in rupture and release of a toxin called haemozoin. These parasites enter the female Anopheles when they bite an infected person. They fertilise and multiply in the stomach wall of mosquito. Sporozoites are now stored in the salivary gland of mosquito till it is again transferred into the human body. Thus malarial parasite is digenetic as it needs 2 hosts to complete its life cycle.
8. What are the main sources of infection of Entamoeba histolytica?
Ans: Drinking water and food contaminated by the faecal matter are the main sources of infection.
9. What is filariasis? State its symptoms.
Ans: Filariasis is a helminthic disease where the parasite lives inside lymph vessels or connective tissues. Its symptoms are
(i) Inflammation of organs in which they live.
(ii) Blockage of lymph vessels of lower limbs resulting in swelling. Lower limbs appear like legs of elephant.
(iii) Genital organs may also be affected, leading to deformation.
10. Write a brief note on how one can prevent occurrence of infectious diseases.
Ans: The various ways are
(i) Maintenance of personal hygiene by keeping the body clean, consuming clean drinking water, food etc.
(ii) Maintenance of public hygiene by proper disposal of waste and excrete etc.
(iii) Eradication of vectors and their breeding places.
(iv) Vaccination and immunisation programmes for diseases like polio, diphtheria etc.
(v) Use of antibiotics and drugs to treat the infected person.
11. What are the different types of barrier in innate immunity?
Ans: The different types of barrier are
(i) Physical barriers: These barriers do not allow pathogens and foreign agents to enter the body. e.g. skin, mucous membranes of digestive, respiratory and urinogenital tract trapping microorganisms.
(ii) Physiological barriers: Acid in the stomach saliva in the mouth, tears from eyes all prevent microbial growth.
(iii) Cellular barriers: WBCs (polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes, natural killer lymphocytes) and macrophages phagocytose and destroy microbes.
(iv) Cytokine barriers: Interferons produced by virus infected cells protect non-infected cells from further viral infection.
12. Define allergy. Name the antibody which is produced during allergy.
Ans: The exaggerated or hypersensitive reaction of the immune system to certain antigens present in the environment is called allergy Ig antibodies are produced during allergy.
13. What is autoimmunity? Name one autoimmune disease.
Ans: Autoimmunity is an abnormal immune response in which the immune system of the body starts attacking and destroying certain cells and molecules as if they are antigens. One autoimmune disease is rheumatoid arthritis.
14. Write the name of the plant and the plant parts from which cannabinoid can be obtained.
Ans: Cannabinoids are obtained from the inflorescence, leaves and the resins of Cannabis sativa.
15. Define drug abuse.
Ans: Taking of drugs for purposes other than clinical use, in amount, concentration or frequency that impairs physical, physiological and psychological functions of the body is called drug abuse.
16. Which system is greatly affected by cannabinoids.
Ans: Cannabinoids are generally taken by inhalation and oral ingestion so they effect the cardiovascular system of the body.
17. Describe the ill effects of smoking.
Ans: (i) Smoking leads to increase in carbon monoxide content of blood and reduces concentration of haem-bound oxygen, as a result of which oxygen deficiency in the body is created.
(ii) It increases the chances of lung cancer, bronchitis, coronary heart disease etc.
18. State how transmission of HIV infection occurs.
Ans: (i) By sexual contact with the infected person.
(ii) By transfusion of contaminated blood.
(iii) By sharing infected needles.
(iv) From infected mother to her child through placenta during pregnancy.
19. Distinguish between :
(a) Humoral immunity and Cell Mediated immunity
Ans :
Humoral Immunity
1. It is mediated by B-lymphocytes
2. The system functions through formataion of antibodies.
3. It is effective against those pathogens that invade body fluids.
4. It has little effect against cancers and transplants.
Cell Mediated Immunity
1. It consists of T-lymphocyte
2. The system functions directly through T-cells.
3. It is effective against those pathogens which pass into host cells.
4. It operates against cancer cells and transplants.
(b) Innate Immunity and Acquired Immunity Ans :
Innate Immunity
1. It is present from birth and is inherited from parents
2. It is non-specific.
3. The innate immunity remains throughout life.
4. The various physical, physio- logical, cellular and cytokine barriers are the bases of innate immunity.
Acquired Immunity
1. It is not present from the birth.
2. It is pathogen specific.
3. The acquired immunity can be short lived or life long.
4. The memory cells formed by B and T-cells are the bases of acquired.
(c) Active immunity and Passive immunity.
Ans:
Active Immunity
1. It is developed due to contact with pathogen or its antigen.
2. It is slow but long lasting.
3. It takes time to develop its response.
4. It has no side effects.
Passive Immunity
1. It is developed when ready made antibodies are injected into the body.
2. It is fast but lasts only for few days.
3. It may cause a reaction.
4. It may cause a reaction.
(d) T-lymphocyte and B-lymphocyte
Ans:
T-lymphocyte
1. T-lymphocytes are preprocessed in thymus gland.
2. Life span is long.
3. Memory persists in T-cells.
4. Antibodies are not produced.
B-lymphocyte
1. B lymphocytes are prepro- cessed in bone marrow.
2. Life span is short.
3. Memory is absent.
4. Plasma cells produce antibodies.
(e) Benign tumour and Malignant tumour
Ans :
Benign tumour
1. It is non-cancerous tumour.
2. This tumour stops growth after reaching a certain age.
3. Benign tumour does not show metastasis and is non invasive
4. It is less fatal to the body.
Malignant tumour
1. It is cancerous tumour.
2. Malignant tumour shows indefinite growth.
3. It shows metastasis and thus invades other body parts.
4. It is more fatal to the body.
20. What is metastasis?
Ans. The phenomenon by which cancerous cells spread through blood from one site to another in order to develop secondary tumour is called metastasis
[E] SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (3 MARKS)
1. Discuss the three criteria which affect the health, causing diseases.
Ans: 1) Genetic disorders deficiencies with which a child is born and deficiencies/defects which the child inherits from parents from birth.
2) Infections and
3) Life style including food and water we take, rest and exercise we give to our bodies, habits that we have a lack etc.
2. What are the different species that cause malaria in man?
Ans: Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malaria and plasmodium falciparum.
3. Diagramatically explain the life cycle of malarial parastie.
Ans:
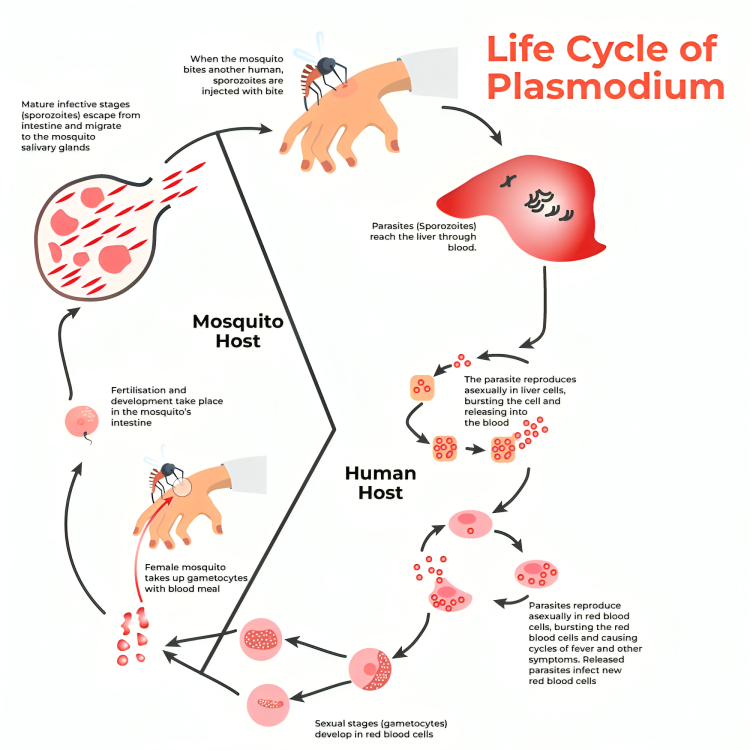
(Stages in the life cycle of Plasmodum)
4. Name the causative organism of amoebiasis. State the symptoms of the disease.
Ans: Amoebiasis is caused by Entamoeba histolytica.
Symptoms
1) Constipation
2) Abdominal pain and cramps
3) Stools with excess mucous and blood clots.
5. Describe the structure of antibody molecule.
Ans: Antibodies are protein molecules called immunoglobulins (Ig) and are of five types IgA, IgM, IgE, IgG and IgD. And antibody has a Y shaped structure. Each antibody molecule consists of four polypeptide chains, two are long called heavy (H) chains while the other two are short called light (L) chains.
Hence an antibody is represented as H2L2.
6. What is immunization? How recombinant DNA technology helps in mass immunization?
Ans: Immunization is the process by which the body produces antibodies against the vaccine (primary response) and develop the ability to neutralise pathogens during actual infection (secondary response)
Recombinant DNA technology has allowed the production of antigenic polypeptides of pathogen in bacteria or yeast. Vaccines produced using this approach allow large scale production and hence greater availability for immunisation e.g. hepatitis B vaccine produced from yeast.
7. Write a note on prevention of AIDS.
Ans: (1) National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) established in 1991 and other NGOs educate people about AIDS.
(2) WHO has started a number of programmes to prevent the spreading of HIV infection that includes-
(i) making blood from blood banks safe from HIV.
(ii) ensuring the use of only disposable needles and syringes.
(iii) free distribution of condoms
(iv) controlling drug abuse
(v) advocating safe sex and promotiong regular check ups.
8. Discuss the causes of cancer.
Ans: The cancer causing agents are called carcinogens.
They are of following types-
(i) Chemical agents in cigarette smoke. Aniline dyes, benzopyrene, chemicals
(ii) Physical agents gamma rays, non-ionising Ionising radiations like X-rays and radiatins like W-rays.
(iii) Biological agents Oncogenic viruses, some parasites.
9. How cancerous growth occurs?
Ans: In our body, cell growth and differentiation is highly controlled and regulated. In cancer cells there is breakdown of these regulatory mechanism. Cancerous cells also lost the property of contact inhibition. As a result cancerous cells just continue to divide giving rise to masses of cells called tumours which are of two types- benign and malignant. Benign tumours do not spread to other parts of the body but malignant tumours grow very rapidly invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues. Cells sloughed from such tumours reach distant sites through blood and wherever they get lodged in the body they start a new tumour there.
10. From which plant cocaine is obtained? Why sportsperson abuse this drug? State the effect of excessive dosage of cocaine.
Ans: Cocaine is obtained from Erythroxylum coca. Sportsperson abuse this drug because it has a potent stimulating action on central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy.
Excessive dosage of cocaine causes headache, convulsions, hallucination and death due to cardiovascular or respiratory failure.
11. Write notes on
(a) Opioids
(b) Cannabinoids
(c) Cocaine
Ans. (a) Opioids: Are the drugs, which bind to specific opioid receptors present in our central nervous system and gastrointestinal tract. Heroin commonly called smack is chemically diacety Imorphine which is a white, odorless, bitter crystalline compound. This is obtained by acetylation of morphine which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant Papaver somniferum. Generally taken by snorting and injection, heroin is a depressant and slows down body functions.
(b) Cannabinoids Are a group of chemicals which interact with cannabinoid receptors present principally in the brain. Natural cannabinoids are obtained from the inflorescences of the plant Cannabis sativa. The flower tops, leaves and the resin of cannabis plant are used in various combinations to produce marijuana, hashish, charas and ganja. Generally taken by inhalation and oral ingestion, these are known for their effects on cardiovascular system of the body.
(c) Cocaine : Cocaine is obtained from coca plant Erythroxylum coca native to South America. It interferes with the transport of the neuro transmitter dopamine cocaine commonly called coke or crack is usually snorted. It has a potent stimulating action an central nervous system, producing a sense of euphoria and increased energy. Excessive dosage of cocaine causes hallucinations.
[F] LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS:
1. What is the infective stage of malarial parasite? Describe the life cycle of malarial parasite in brief. (5 MARKS)
Ans: The infectious stage of malarial parasite is sporozoites. Plasmodium enters the human body as sporozoites through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito. The parasites initially multiply within the liver cells and then attack the red blood cells resulting in their rupture. The rupture of RBC is associated with release of a toxic substance, haemozoin, which is responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days. When a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected person, these parasites enter the mosquito’s body and undergo further development. The parasites multiply within them to form sporozoites that are stored in their salivary glands. When these mosquitoes bite a human, the sporozoites are introduced into the human body and the cycle is repeated again.
2. How a healthy person acquires pneumonia? State the symptoms of pneumonia.
Ans: Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophetus influenzas are responsible for the disease pneumonia in humans which infects the alveoli of the lungs. As a result of the infection, the alveoli get filloed with fluid leading to severe problems in respiration. A healthy person acquires the infection by enhaling the droplets/aerosols released by an infected person or even by sharing glasses and utensils with an infected person.
Symptom__
1) Fever
2) Chills
3) Cough
4) Headache
5) In severe cases, the lips and finger nails may turn gray to bluish in colour.
3. Discuss the immune system of the body with neat labelled diagram.
Ans: Components of immune system are-
(i) Lymphoid organs
(ii) Immune Cells
(iii) Soluble molecules like antibodies
(iv) Lymphoid tissues.
1. Lymphoid organs: It is of two types-
(i) Primary lymphoid organs The organs where lymphocytes originate and mature to become antigen sensitive. e.g. bone marrow and thymus.
(a) Bone marrow: It is the primary lymphoid organ where all blood cells including lymphocytes originate. Bone marrow provides the micro environment for the development and maturation of B-lymphocytes.
(b) Thymus: It is a lobed organ which is quite large at the time of birth but reduces with age. It provides the micro- environment for the development and maturation of T- lymphocytes.
(ii) Secondary lymphoid organs: The organs where lymphocytes interact with the antigen and proliferate to become effector cells.
(a) Spleen: It contains lymphocytes and phagocytes and acts as a filter of the blood by trapping blood born microbes. It has a large reservoir of erythrocytes.
(b) Lymph nodes: These are present along the lymphatic system and trap the microorganisms or other antigens that enter the lymph and tissue fluid. Antigens trapped in the lymph nodes activate the lymphocytes and produce an immune response.
(iii) Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT): It is formed of masses of lymphoid tissue lining the mucosa of respiratory, digestive and urinogental tracts.

(Diagrammatic representation of Lymph nodes)
4. Name the causative organisms of AIDS.
Ans: AIDS is caused by the Human Immuno Deficiency Virus (HIV), a member of a group of viruses called retrovirus, which have an envelope enclosing the RNA genome. Transmission of HIV infection generally occurs by
(i) sexual contact with the infected person.
(ii) transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products.
(iii) sharing infected needles
(iv) from infected mother to her child through placenta.
So people who are at high risk of getting this infection includes-
(i) individuals having multiple sexual partners
(ii) drug addicts who take drugs intravenously
(iii) individual who requires repeated blood transfusion
(iv) children born to an HIV infected mother.
5. Describe the mechanism of HIV infection.
Ans: After getting into the body of a person, the virus enters the macrophages. Here RNA is replicated to form viral DNA by enzyme reverse transcriptase. The viral DNA now gets incorporated into the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce viruses. The macrophages continue to produce virus particles. The virus particles enter helper T-lymphocytes (TH cells) in the blood, where they continue to replicate and produe viral progenies. Thus the number of helper T-lymphocytes progressively decreases in the body of the infected person. With the decrease in number of T-cells, the immunity also decreases. The person is unable to produce any immune response even against common bacteria like Mycobacterium parasites like Toxoplasma, viruses and fungi.
6. How cancer can be diagnosed? Discuss the treatments of cancer.
Ans: Cancer can be diagnosed by –
(i) Blood and bone marrow tests are done for increased cell counts in case of leukemias.
(ii) Histopathological study or biopsy- In biopsy a piece of the suspected tissue cut into thin sections is stained and examined under microscope by a pathogist.
(iii) Radiography-X-rays are used to detect cancer of the internal organs.
(iv) Computed tomography It uses X-rays to generate a three dimensional image of the internal of an object.
(v) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Non-ionising radiations and strong magnetic field are used in MRI to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissue.
(vi) Monoclonal antibodies antigens against cancer specific antigens are also used for detection of certain cancers.
CANCER TREATMENT
(i) Surgery: The tumour cells are removed with the help of surgery to check the spread of cancerous cells.
(ii) Radiation therapy: A lethal irradiation of tumour cell is done, taking proper care of the normal tissues surrounding them.
(iii) Chemotherapy: Cancerous cells are killed by several chemotherapeutic drugs.
(iv) Immunotherapy: In this method biological modifiers like a-interferons are used which activate the immune system and help in destroying the tumour.
7. What is adolescence? Write an essay on adolescence and abuse of drugs/alcohol.
Ans: The period between 12-18 years of age is thought of as adolescence period. Adolescence is also considered as the bridge linking childhood and adulthood. It is accompanied by several biological and behavioural changes. Thus adolescence is a very vulnerable phase of mental and psychological development of an individual.
Curiosity, need for adventure and excitement and experimentation constitute common causes which motivate youngsters towards drug and alcohol abuse. Thus, the first use of drugs or alcohol may be out of curiosity or experimentation, but later the child starts using these to escape facing problems. Also stress from pressures to excel in academics or examinations has played a significant role in persuading the youngsters to try alcohol and drugs. The perception among youth that it is ‘cool’ or progressive to smoke, use drugs or alcohol is also a major cause to start these habits. T.V. movies, newspapers, internet also promote this perception. Other factors associated with drug and alcohol abuse are unstable or unsupportive family structures and peer pressure.
8. State the effects of drug/alcohol abuse.
Ans: 1. The immediate effects are manifested as reckless behaviour, vandalism and violence.
2. Excess doses can lead to coma and death due to cerebral haemorrhage, respiratory and heart feature.
3. A combination of drugs or their intake with alcohol leads to death.
4. The most common warning signals include-
(i) Drop in academic performance.
(ii) Lack of interest in personal hygiene.
(iii) Withdrawal and isolation from family.
(iv) Aggressive and rebellious behaviour.
(v) Change in sleeping and eating habits.
(vi) Fluctuations in weight.
5. When the drug is taken intravenously it can lead to infections like AIDS and hepatitis.
6. Chronic use of drug and alcohol damages nervous system and liver (cirrhosis) and the alcoholism during pregnancy affects the foetus.
7. Use of alcohol during adolescence can lead to heavy drinking in adulthood.
8. Drugs causes various side effects in males such as acne, aggressiveness, reduction in size of testicles, decreased sperm production premature boldness, enlargement of prostrate gland.
9. Drugs causes side effects in females also such as masculinisation, aggressiveness, depression, abnormal menstrual cycles, excessive facial and body hair etc.
9. Discuss the various means of prevention and control of drug and alcohol abuse.
Ans: The various means are (i) Avoid undue peer pressure: A child should not be pushed unduly to perform beyond his/her threshold limits.
(ii) Education and Counselling: Educating and counselling to face problems and stresses and to accept disappointments and failures as a part of life. Also it would be worthwhile to channelise the child’s energy into healthy pursuits like sports, music, reading etc.
(iii) Seeking help from parents and peers: It could help to vent their feelings of anxiety and guilt and could get proper advice to eat sort out their problems.
(iv) Looking for danger signs: Danger signs should be identified which will help in proper remedial steps or treatment.
(v) Seeking professional and medical help: Psychologists, psychiatrists and deaddiction and rehabilitation programmes helps affected individuals with sufficient efforts and will power to get rid of the problem completely and lead a perfectly normal and healthy life.
10. State the causes of cancer.
Ans. Transformation of normal cells into concur neoplastic cells may be induced by physical, chemical or biological agents. These agents are called carcinogens. Ionising radiations like X-rays and gamma rays and non ionizing radiations like UV cause DNA damage leading to neoplastic transformation. The chemical carcinogens present in tobacco smoke have been identified as a major course of lung cancer. Cancer causing viruses called oncogenic viruses have genes called viral oncogenes. Furthermore several genes called cellular ensconces or proto oncogenous have been identified in normal cells which when activated under certain conditions could lead to oncogenic transformation of the cells.
-0000-
Last Words on AHSEC Class 12 Biology Chapter: 7 Human Health and Diseases
The Chapter 7 of AHSEC Class 12 Biology deals with Health and Diseases in Humans for a brief understanding. You can Download this HS 2nd Year Biology Notes in PDF 2025.

