Get AHSEC Class 12 Biology Chapter: 12 Ecosystems Important Questions Answers 2025. In this Post we have Prepared for you Assam Board Biology Chapter: 12 Solution as Per AHSEC Latest Syllabus and exam patterns.
AHSEC Class 12 Biology Chapter: 12 Ecosystems Solution Can be a great resource for your exam preparation. Use this chapter’s Notes/Solution as a guideline or reference.
An Overview of AHSEC Class 12 Biology Notes for 2025
| Name of Board | AHSEC |
| Class: | Assam Board Class 12 |
| Subject: | AHSEC Class 12 Biology |
| Number of Chapter: | 12 |
| Chapter Name | Ecosystems |
| Content Type: | Text, Images and PDF Format |
| Academic Year: | 2024-25 |
| Medium: | English |
| Available Solution Link: | AHSEC Class Biology Notes |
AHSEC Class 12th Biology Chapter: 12 Ecosystems
[A] FILL IN THE BLANKS. (1 MARK EACH)
1. Many individuals of a species living together in a defined area form_____
Ans. Population.
2. Net primary productivity (NPP) = ______Respiration (R).
Ans. GPP (Gross primary poductivity)
3. Process of breakdown of detritus into smaller particles is called_____
Ans. Decomposition.
4. ______is the process by which bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simple inorganic substances.
Ans. Catabolism
5. The mass of living material at a particular time in a trophic level is called _____
Ans. Standing crop.
6. Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally_____
Ans. Inverted.
7. Out of the total cost of various ecosystem services, the soil formation accounts for about per cent.
Ans. 50%.
8. Vertical distribution of different species occupying dif- ferent levels is called____
Ans. Stratification
9. Of the incident solar radiation (on earth)less than 50% of it is_____
Ans. Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR)
[B] TRUE OR FALSE (1 MARK EACH)
1. Horizontal distribution of different species occupying in different spatial position is called stratification.
Ans. False
2. Marginal plants are autotrophic components of a pond ecosystem.
Ans. True
3. Fragmentation, leaching and catabolism during decomposition operate sequentially one after another.
Ans. Truc
4. Flow of energy in ecosystem is unidirectional.
Ans. True
5. Photosynthetic activation radiation constitutes less than 50% of the incident solar radiation.
Ans. True
6. Grasses, are usually pioneer species in primary succession on rocks.
Ans. False
[C] VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS: (1 MARK EACH)
1. What is ecosystem?
Ans. Ecosystem is a self regulated and self sustaining structural and functional unit of nature where living organisms interact and exchange materials among thereselves and with their physical environment.
2. What are the two basic categories of ecosystem?
Ans. Terrestrial and equatic are the two basic categories of ecosystem.
3. What are the autotrophic components of pond ecosystem?
Ans. Phytoplanktons, some algae and the floating, submerged and marginal plants found at them edges.
4. At which part of a pond ecosystem decomposers are abundant?
Ans. In the bottom of the pond.
5. Define gross primary productivity.
Ans. Gross primary productivity is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis.
6. What is net primary productivity?
Ans. Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs.
7. Explain the process of leaching during decomposition.
Ans. By the process of leaching water soluble inorganic nu- trients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as un- available salts.
8. Define mineralization during decomposition.
Ans. Mineralization is the process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes to release inorganic nutrients.
9. Which type of food chain is dominant in sea?
Ans. Grazing food chain.
10. How much photosynthetically active radiation (in percentage) is captured by plants?
Ans. 210 per cent.
11. Except deep sea what is the only energy source for all ecosystems?
Ans. Sun is the only energy source.
12. Why measurement of biomass in terms of dry weight is more accurate?
Ans. Dry weight is more accurate as it avoids seasonal varia- tions in moisture content of biomass.
13. What are green plants known as?
Ans. Producers.
14. What is the role of fungi in an ecosystem?
Ans. Fungi act as decomposers and help in degrading dead organic matter.
15. What is trophic level?
Ans. Specific place occupied by the organisms in the food chain based on the source of their nutrition is called trophic level.
16. What is ecological succession?
Ans. The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession.
17. What are the different types of succession?
Ans. Primary and Secondary succession.
18. What is climax community?
Ans. The final community that is in near equilibrium with the environment is called climax community.
Q.19. Which type of food chain is dominant in sea?
Ans. Secondary succession is faster than primary succession because of the presence of
(i) Soil for growth, which also results in quick attainment of climax.
(ii) Water, the necessary environment and seeds or other progagules are also present.
[D] SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (2 MARKS EACH)
1. Define vertical stratification with example.
Ans. Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called vertical stratification. For eg, trees occupy top ver tical strata or layer of a forest, shrubs the second and herbs and grasses occupy the bottom layers.
2. State the functional components of ecosystem.
Ans. The functional components of ecosystem are –
(i) Productivity: The rate of biomass production.
(ii) Decomposition: The process of breaking down complex organic matter into inorganic substances.
(iii) Energy flow: The transfer of energy from one trophic level to another.
(iv) Nutrient cycling: The movement of nutrient elements through various components of an ecosystem.
3. What are the different types of primary productivity? State the relation between them.
Ans. The different types of primary productivity are Gross primary productivity: The rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis.
Net primary productivity: It is the available biomass for the consumption of heterotrophs.
The relation between them is GPPR NPP.
4. Why earthworm is called as “Farmer’s Friend”?
Ans. Earthworm is called as the farmer’s friend because they help in the breakdown of complex organic matter as well as in loosening of the soil.
5. What is the raw material for decomposition called? What are its components?
Ans. Detritus is the raw material for decomposition. Its components are dead plant remains such as leaves, bark, flowers and dead remains of animals, including faecal matter.
6. What is humus? State its importance.
Ans. Humus is a dark coloured amorphous partially decomposed organic matter that is highly resistant to microbial action.
Humus is slightly acidic, colloidal and functions as reservoir of nutrients. It releases small quantities of nutrients into the soil that can be readily absorbed by plants.
7. What is Standing crop? How is it measured?
Ans. The amount of living matter (biomass) present at every trophic level at a particular time is known as standing crop.
It is measured as the mass of living organisms (biomass) or the number in a unit area.
8. Define 10% law of energy flow. Why the number of levels in a grazing food chain is restricted?
Ans. The passage of about 10% of biomass energy from one trophic level to the next is called 10% law.
The number of trophic levels in a grazing food chain is restricted as the transfer of energy follows 10% law, thus the energy abvailability becomes insufficient in the next trophic levels.
9. Which type of pyramid is always upright and why?
Ans. Pyramid of energy is always upright because when energy flows from a particular trophic level to the next trophic level some energy is always lost as heat at each step.
10. In a nutshell how can you define Ecosystem services?
Ans. Ecosystem services are benefits provided by ecosystem processes to environment in its cleaning and maintenance, enhancing aesthetic beauty, maintenance of biodiversity, protection of soil water and land resources besides providing a habitat to wildlife.
11. What is food web? How it differs from food chain?
Ans. Food web is a network of food chains which become interconnected at various trophic levels so as to form a number of feeding connections amongst the different organisms of a biotic community.
Whereas a food chain is a sequence of organisms of an ecosystems through which the food and its contained energy passes with each member becoming the food of a later member of the sequence.
12. Why energy is less at secondary consumer level than the producer?
Ans. Producers belongs to the first trophic level from which energy is transferred to the next higher trophic levels. But as energy transfers from one trophic level to the next, it follows the ten per cent law and the amount of energy decreases at successive trophic levles. So energy is less at secondary consumer level than the producers.
13. What is a sedimentary cycle?
Ans. The nutrient cycle in which materials involved in circulation between biotic and abiotic components of biosphere are non gaseous and the reservoir pool is lithosphere. eg. Phosphorus, Calcium etc.
14. State the difference between grazing food chain and detritus food chain.
Ans. Grazing food chain
(i) The chain begins with producers as the first trophe level.
(ii) It is the major conduit for energy flow in aquatic ecosystems.
Detritus food chain
(i) The chain begins with detritivores and decomposers as the first trophic level.
(ii) It is the major conduit for energy flow in terrestial ecosystem.
15. Distinguish between primary and secondary succession.
Ans. Primary
(i) It occurs in an area which has been bare from the beginning.
(ii) Soil is absent at the time of beginning of primary succession.
Secondary
(i) It occurs in an area which has been denuded recently.
(ii) Soil is present in the area where secondary succession begin.
16. Distinguish between hydrarch succession and xerarch succession
Ans. Hydrarch
(i) It occurs in freshly formed water body.
(ii) Pioneer species generally belong to phytoplankton.
Xerarch
(i) It occurs over bare rock.
(ii) Pioneer species are generally lichens.
17. What are different levels of consumers? In grazing food chain what is the position of a goat?
Ans. The different levels of consumer are-
(i) Primary consumer (Herbivores)
(ii) Secondary consumer (Carnivores)
(iii) Tertiary consumer (Top carnivore)
In grazing food chain goat occupy the position of primary con- sumer.
18. State the factors for invasion of species in secondary succession.
Ans. The factors for invasion of species in secondary succes- sion are-
(i) Condition of the soil
(ii) Availability of water.
(iii) The environment
(iv) Seeds or other propagules present.
[E] SHORT ANSWER QUESTION (3 MARKS EACH)
1. What is productivity? How the productivity of an ecosystem is expressed?
Ans. The rate of biomass production is called productivity.
It is expressed in terms of g/m²/yr or Kcal/m²/yr to compare the productivity of different ecosystems.
2. Write briefly the factors controlling primary productivity of ecosystem.
Ans. The factors controlling primary productivity are
(i) Plant species inhabiting a particular area.
(ii) Availability of nutrients Nutrients are essential for growth of producers. Nitrogen is deficient in oceans that limits productivity in marine ecosystems.
(iii) Photosynthetic capacity of plants – C₁ plants are more productive than C, plants.
(iv) Variety of environmental factors like solar radiation, temperature etc: In aquatic ecosystems productivity is less than terrestrial ecosystem. It is limited by light which decreases with increasing water depth. Temperate forests have lesser productivity than tropical rain forests.
3. Explain the factors controlling the decomposition.
Ans. The factors controlling decomposition are
(i) Temperature: A temperature of 25°C and more hastens decomposition while a temperature less than 10°C reduces rate of transpiration.
(ii) Moisture Warm and moist environment favour decomposition.
Temperature and soil moisture are the most important climatic factors that regulate decomposition through their effects on the activities of soil microbes.
(iii) Chemical composition: The rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus. If detritus is rich in lignin and chitin decomposition rate is slower while if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water soluble substances like sugars, decomposition rate is quicker.
(iv) Aerobiosis: Aerobic conditions are essential for activity of decomposer organisms because decomposition is oxygen requiring process.
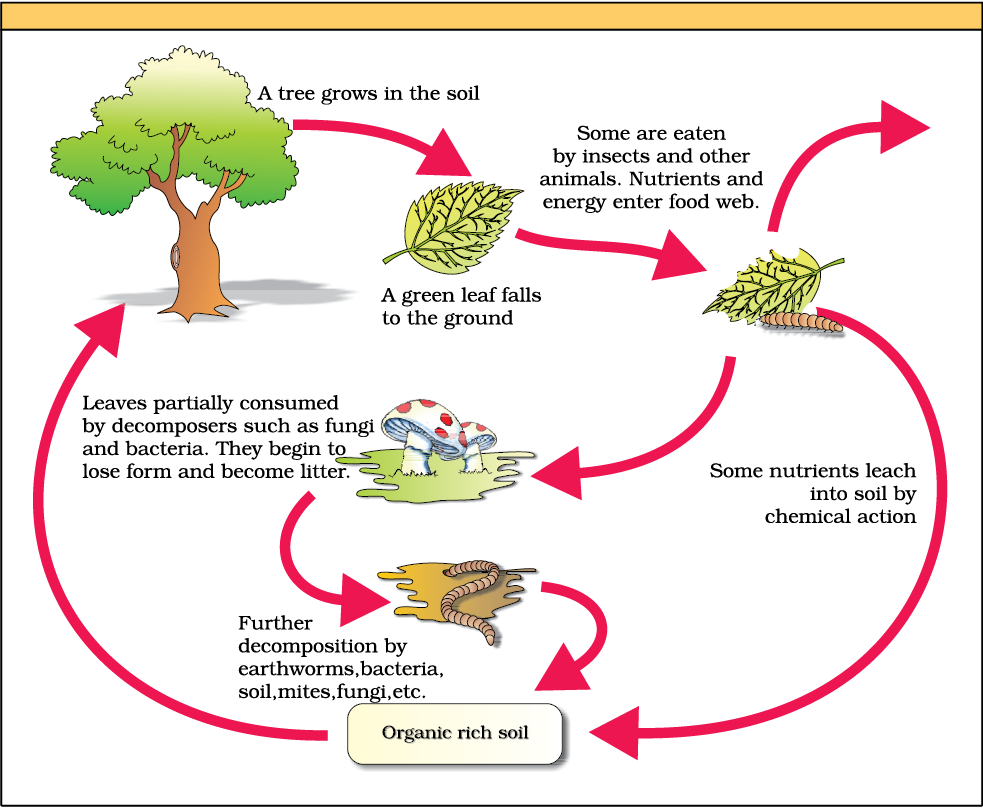
4. Diagrammatically explain decomposition cycle in a terrestrial ecosystem.
Ans:-
5. What is food chain? Describe the two basic types of food chain with examples.
Ans. A food chain is a sequence of trophic levels of an ecosystem through which the food and its contained energy passes from producers to ultimate consumers.
Two basic types of food chain are
(i) Detritus food chain It begins with detritus or dead organic matter. Detritivores and decomposers feed over it. Therefore, food energy present in detritus passes into them by degradation of the dead organic matter. Decomposers secrete digestive enzymes that breakdown dead and waste materials into simple, inorganic materials, which re subsequently absorbed by them
. For eg.
Detritus → Earthworm Sparrow → Falcon.
(ii) Grazing food chain: It is the most common food chain. It is also called predator food chain as predation occurs at every step. It is composed of producers, consumers and decomposers. GFC is the major conduit of energy flow in aquatic ecosystem. For. eg.
Grass grasshopper → Frog → Snake Peacock
6. Where do you get inverted pyramid? Describe briefly an inverted pyramid of number.
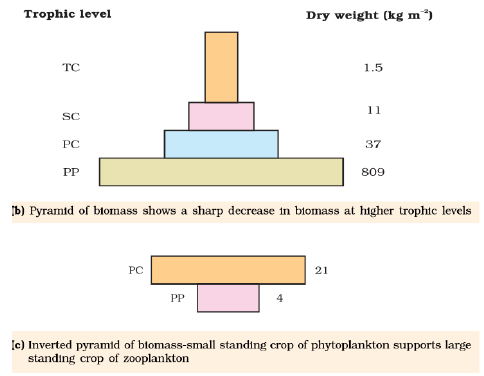
Ans. Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally inverted because the biomass of fishes far exceeds that of phytoplankton. Sometimes pyramid of number can also be inverted. For eg.
A single large sized tree which is the producer can provide nourishment to several herbivores (eg. birds). The birds may support a still larger population of ectoparasites. Such a pyramid is inverted.
7. Describe the primary succession in water.
Ans. The various stages of primary succession in water are
(i) Plankton stage: It is the pioneer stage spores of this stage reach the water body through wind or animals. The first to appear are minute autotrophic organisms called phytoplanktons. Death and decomposition of plankton produce organic matter.
(ii) Submerged stage: The bottom lined by soft mud having organic matter is favourable for growth of submerged plant.
(iii) Floating stage: Floating leaved anchored plants appear where water becomes shallow.
(iv) Reed swamp stage: Amphibious plants grow where the water body becomes shallow.
(v) Marsh meadow stage: The shores built up by reed swamp stage are invaded by sedges.
(vi) Scrub stage: Shrubs and small trees which can tolerate bright sunlight invades next.
(vii) Climax forest: New trees invade the area which forms the climax community.
8. Explain the carbon cycle.
Ans. Carbon constitutes 49% of dry weight of an organism. 71% of the carbon is found dissolved in oceans which is responsible for its regulation in atmosphere. The carbon cycle occurs through atmosphere, ocean and through living and dead organisms. It is estimated that 4 x 1013 Kg of carbon is fixed in the biosphere through photosynthesis annually Carbon is returned to atmosphere is CO, by animals and plants through respiration and the activity of the decomposers.
Some amount of fixed carbon is lost as sediments and removed from circulation. Burning of wood, forest fire, volcanic activity and combustion of organic matter and fossil fuels are some essential sources for releasing CO, in the atmosphere.
9. What is nutrient cycling? What are the different types of nutrient cycling? Give one example of each of them.
Ans. The movement of nutrient elements through the various components of an ecosystem is called nutrient cycling.
The different types of nutrient cycles are-
(i) Gaseous: The reservoir for gaseous type of nutrient cycle exists in the atmosphere. For eg. Carbon cycle.
(ii) Sedimentary: The reservoir for sedimentary cycle is located in Earth’s crust. eg. Phosphorus cycle.
10. Describe the phosphorus cycle.
Ans. The natural reservoir of phosphorus is rock which contains phosphorus in the form of phosphates. When rocks are weathered, mintue amounts of these phosphates dissovle in soil solution and are absorbed by the roots of the plants. Herbivores and other animals obtain this elements from plants, The waste products and the dead organisms are decomposed by phosphate solubilising bacteria releasing phosphorus.
11. Write briefly on ecosystem services.
Ans. The products of ecosystem processes are called ecosystem services. Forests are the major source of ecosystem services. They help to –
(i) purify air and water.
(ii) mitigate droughts and floods.
(iii) Cycle nutrients.
(iv) generate fertile soils.
(v) provide wildlife habitat.
(vi) Maintain biodiversity.
(vii) pollinate crops.
(viiii) provide aesthetic, cultural and spiritual values.
12. “Flow of energy in ecosystem follows the laws of thermodynamics”, explain the statement.
Ans. The first law of termodynamics state that energy can neither be created nor destroyed but it can be transferred and transformed from one component to another and from one frorm to another. Thus energy of sunlight is changed into chemical energy of food and heat As food energy passes from one trophic level to the next.
According to 2nd law no transfer or tansformation of energy occurs unless and until it is accompanied by degradation of energy from concentrated to dispersed form. Energy of food is in concentrated form while it is highly dispersed form in heat. The transfer of food energy from one trophic level to another is accompanied by degradation and loss of major part of food energy as heat.
[F] LONG ANSWER QUESTION (5 MARKS EACH)
1. Why is the pond regarded as a classic example of ecosystem? Explain pond as an example of ecosystem.
Ans. Pond is regarded as a classic example of ecosystem because it is a self sustainable unit that explain the complex interactions that exist in an aquatic ecosystem.
A pond is a shallow water body in which all four basic components of an ecosystem are well exhibited. The abiotic component is the water with all the dissolved inorganic and organic substances and the rich soil deposit at the bottom of the pond. The solar input, the cycle of temperature, day length and other climatic conditions regulate the rate of function. The autotrophic components include the phytoplankton, some algae and the floating, submerged and marginal plants found at the edges. The consumers are represented by the zooplankton, the free swimming and bottom dwelling forms. The decomposers are the fungi, bacteria and flagellates abundant in the bottom of the pond.
This system performs all the functions of an ecoystem, i.e. conversion of inorganic into organic material with the help of radiant energy of the sun by the autotrophs; consumption of the arutotrophs by heterotrophs, decomposition and mineralisation of the dead matter to release them back for reuse by the autotrophs.
2. What is decomposition? Explain the process of decomposition.
Ans. The process of breaking down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like CO₂, water and nutrient is called decomposition.
The decomposition process takes place in the following steps
(i) Fragmentation: The process af breaking down of detritus into smaller particles by detritivores, e.g. earthworm.
(ii) Leaching: The process by which water soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
(iii) Catabolism: It is the process in which degradation of detritus into simpler inorganic substances takes place by the action of bacterial and fungal enzymes.
(iv) Humification: The process of accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance called humus that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate is called humification.
(v) Mineralisation: The process by which humus is further degraded by some microbes to release inorganic nutrients is caled mineralisation.
3. How energy flow occurs in an ecosystem? Depict the energy flow through necessary diagrammatic representation.
Ans. The sun is the only source of energy for all ecosystems on earth. Out of the total incident solar radiation only 50% of it is photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) and this small amount of energy sustain the entire living world. So there is undirectional flow of energy from the sun to producers and then to consumers. The energy is transferred in an ecosystem in the form of food which is degraded and lose major part of food energy us heat during metabolic activities and only a very small fraction becomes stored as biomass.
The green plants in the ecosystem which can trap solar energy to convert it into chemical energy are called producers. All the
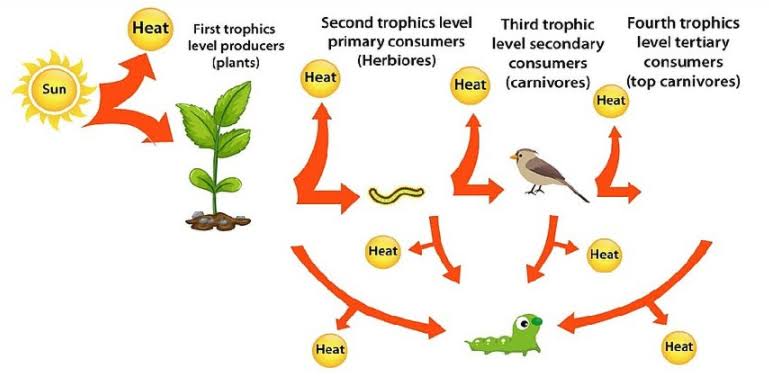
animals that depend for food on plants are called consumers. Consumers are further divided into primary, secondary and tertiary consumers. At each step of food chain when food energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next higher trophic level only about 10% of energy is passed on to next level.
4. What is ecological pyramid? Explain different types of pyramids with necessary diagrams.
Ans. The relation between producers and consumers in an ecosystem can be graphically represented in the form of a pyramid called ecological pyramid. The base of the pyramid always represents the producers or the first trophic level and the apex represents top level consumer or the last trophic level. The differenct types of pyramids are
(i) Pyramid of number: The relationship between producers and consumers in an ecosystem can be represented in the form of a pyramid in terms of number called pyramid of number.
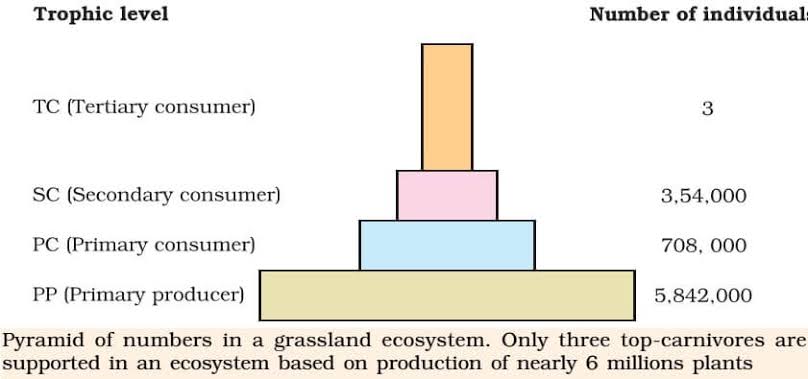
(ii) Pyramid of biomass: The relationship between biomass present sequence wise per unit area of different trophic levels with producers at the base and top carnivores at the tip. It can be-
(a) Upright eg. grassland ecosystem.
(b) Inverted eg. pond ecosystem.
(iii) Pyramid of Energy: It is a graphic representation of amount of energy trapped per unit time and area in different trophic levels of a food chain.

An ideal pyramid of energy. Observe that primary producers convert only 1% of the energy in the sunlight available to them into NPP
5. What do you mean by an Ecosystem? Describe the different components of an Ecosystem.
Ans. Ecosystem is a self sustained and self regulated functional unit where living organisms interact and exchange materials among themselves and with their physical environment.
The different components of ecosystem are
i) Biotic components: They constitute all the living members of an ecosystem. They are three types
(a) Producers (Autotrophs) – They are photosynthetic or autotrophic plants which are able to synthesise organic food from inorganic raw materials with the help of solar radiation. Producers are also called transducers because they are able to change light energy into chemical energy.
(b) Consumers (Heterotrophs) They feed on other organisms for obtaining nourishment. Consumers can be –
(i) Primary consumers or Herbivores.
(ii) Secondary consumers or Primary carnivores.
(iii) Tertiary consumers or secondary carnivores.
(iv) Quarternary consumers or Top carnivores.
(c) Decomposers: They are saprotrophs which feed on dead bodies of organisms to obtain nourishment.
ii) Abiotic Components: They are factors and materials of the physical environment. The materials include inorganic nutrients (eg. carbon nitrogen, oxygen etc) and organic remains Organic remains consists of carbohydrates, proteins etc. Abiotic factors include climatic factors, edaphic factors and topographic factors. The important climatic factors are light, temperature, humidity & water, Edaphic factors include soil.
6. Explain in brief the process of ecological succession on bare rocks.
Ans. Ecological succession on a bare rock is called xerarch succession. The various stages are
(i) Lichen stage: Lichen propagules settle over the rock surface after the rain or heavy dew. They get attached to rock by means of rhizoids. These lichens secrete lichen acids and carbonic acids which corrode rock surface and release minerals thus producing small depressions. These depressions become gathering site for organic matter, dust particles and water.
(ii) Moss stage Lichens growing or rocks make the condition favourable for mosses growth. Mosses accumulate more soil and organic matter. Weathering and fragmentation of rock starts further.
(iii) Annual grass stage: A number of xerophytic grasses and herbs reach the rocks surface occupied by mosses thereby replacing them. Due to increased moisture soil becomes favourable for growth of annual grasses..
(iv) Perennial grass stage: The perennial grasses and herbs are taller. Their roots penetrate deeper. As a result more soil is built up and more moisture becomes available.
(v) Shrub stage: Hardy xerophytic shrubs invade the area occupied by perennial grasses.
(vi) Climax Forest: Initially light tolerant small trees grow after the shrub stage later on larger trees become abundant thus forming a climx forest.
7. Write about the ecosystem service
Ans. Healthy ecosystems are the base for a wide range of economic, environmental and aesthetic goods and services. The products of ecosystem processes are named as ecosystem services forests are the major source of ecosystem services. They-
(i) Purify air and water.
(ii) mitigate droughts and floods.
(iii) cycle nutrients.
(iv) generate fertile soils.
(v) provide wildlife habitat
(vi) maintain biodiversity
(vii) pollinate crops.
(viii) provide storage site for carbon.
(ix) Provide aesthetic, cultural and spiritual values.
Robert constanza and his colleagues tried to put price tags on nature’s life support services which came up to US$ 33 trillion a year. This is nearly twice the value of the global gross national product GNP which us US $ 18 trillion.
Out of the total cost of various ecosystem services, the soil formation accounts for 50%, recreation and nutrient cycling are less than 10% each. The cost of climate regulation and habitat for wildlife are about 6% each.
Q. GIVE ONE WORD TECHNICAL TERM: (SPECIAL 1 MARK QUESTIONS)
1. Group of organisms of one species occupying a definite area.
Ans. Population.
2. A group of organisms belonging to a number of different species.
Ans. Biotic community.
3. A community of organisms, their physical environment interacting as a unit.
Ans. Ecosystem.
4. Green photosynthetic organisms forming the first trophic level.
Ans. Producers.
5. The stored plant energy after respiratory utilization.
Ans. Net primary productivity.
6. A series of eating and being eaten.
Ans. Food Chain.
7. Network formed by interacting food chains.
Ans. Food Web.
8. Total mass of organisms- fresh or dry weight.
Ans. Biomass.
-0000-
Last Words on AHSEC Class 12 Biology Chapter: 12 Ecosystems
The Chapter 12 of AHSEC Class 12 Biology deals with Ecosystems for a brief understanding. You can Download this HS 2nd Year Biology Notes in PDF 2025.