In this post we have cover Gauahti University BCom 2nd Semester Principles of Marketing NEP FYUGP Notes Unit- 3: Product Planning and Pricing Important Notes. Which can be very useful during your preparation. Use this notes as reference any score good marks in your examination.
UNIT – 3: PRODUCT PLANNING AND PRICING
1.. What do you mean by product? State the characteristics of product. Discuss the various stages of a new product development. 2015, 2016, 2019,2021,2022
ANSWER – A product is a tangible or intangible item that is offered to the market for consumption or use, typically to satisfy a want or need. It can be a physical object, a service, or a combination of both.
Characteristics of a Product:
1. Tangibility: Products can be physical goods that you can touch and feel, or they can be intangible services.
2. Utility: Products provide some form of value or benefit to the consumer, addressing a specific need or want.
3. Features: Products have attributes or characteristics that distinguish them from competitors and meet customer requirements.
4. Quality: Product quality refers to how well the product performs its intended function and meets customer expectations.
5. Branding: Products often have brand identities and associations that influence consumer perception and loyalty.
6. Life Cycle: Products go through a life cycle, including introduction, growth, maturity, and decline stages.
Stages of new product development:
1. Idea Generation: The process begins with generating ideas for new products or improvements to existing ones. This can come from various sources, such as customer feedback, market research, or internal brainstorming.
2. Idea Screening: In this stage, ideas are evaluated to identify those with the most potential. Criteria like feasibility, market demand, and alignment with company goals are considered.
3. Concept Development and Testing: The selected ideas are further developed into product concepts. These concepts are tested with a sample of the target market to gauge interest and gather feedback.
4. Business Analysis: A detailed analysis of the potential product’s financial viability is conducted. This includes cost estimation, revenue projections, and a break-even analysis.
5. Product Development: Once a concept is approved, the product is developed. This stage involves designing the product, creating prototypes, and ensuring it meets quality and regulatory standards.
6. Market Testing: The product is tested in a real market environment with a limited release to assess its performance, gather user feedback, and make necessary adjustments.
7. Commercialization: If the product performs well in testing, it moves to the commercialization stage. This involves full-scale production, marketing, and distribution.
8. Launch: The product is officially introduced to the market through various marketing and promotional activities.
9. Post-Launch Evaluation: After the product is in the market, ongoing monitoring and evaluation are essential to track its performance, gather customer feedback, and make improvements as necessary.
2. What do you mean by product planning and development? What are its objectives? State the factors to be considered while developing new product. 2021
ANSWER – Product planning and development refer to the strategic process of creating, improving, or extending products to meet consumer needs and achieve business goals. It involves the conceptualization, design, testing, and launch of new products or enhancements to existing ones.
Objectives of product planning and development:
1. Meet Customer Needs: Develop products that address the specific needs and wants of target customers.
2. Competitive Advantage: Create products that differentiate the company from competitors and provide a competitive edge.
3. Profitability: Generate revenue and profit for the organization through successful product launches.
4. Growth: Drive business growth by expanding product lines, entering new markets, or reaching new customer segments.
5. Innovation: Foster innovation by introducing novel or improved products that stay ahead of market trends.
6. Risk Management: Minimize the risks associated with product development by conducting thorough analysis and testing.
Factors to consider while developing new products:
1. Market Research: Understand the market, customer preferences, and trends to identify opportunities and gaps.
2. Target Audience: Define the ideal customer profile and segment the market accordingly.
3. Feasibility: Assess the technical, operational, and financial feasibility of the new product.
4. Competitive Landscape: Analyze competitors, their offerings, and potential threats to your product’s success.
5. Cost Analysis: Determine the cost of development, production, and marketing, ensuring profitability.
6. Regulatory Compliance: Be aware of industry regulations and ensure the product complies with relevant standards.
7. Intellectual Property: Protect intellectual property through patents, trademarks, or copyrights if necessary.
8. Design and Prototyping: Create product designs and prototypes to visualize and test the concept.
9. Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing to ensure the product meets quality and performance standards.
10. Marketing and Positioning: Develop a marketing strategy to effectively position and promote the product in the market.
11. Launch Strategy: Plan the product’s launch, including timing, distribution, and promotional activities.
12. Post-Launch Support: Consider customer support, warranties, and ongoing product improvement after the launch.
13. Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and challenges in the development process and devise contingency plans.
14. Product Life Cycle: Understand the expected life cycle of the product and plan for future phases.
15. Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental and ethical aspects of the product’s development and usage.
3. What is product life cycle? Explain the different stages of product life cycle (PLC). What is marketing house strategy at each stage? 2016, 2018,2021,2022
ANSWER – The product life cycle is the process a product goes through from when it is first introduced into the market until it declines or is removed from the market. The life cycle has four stages—introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
While some products may remain in a prolonged maturity state for some time, all products eventually phase out of the market due to several factors including saturation, increased competition, decreased demand, and dropping sales.
Companies use PLC analysis (the process of examining their product’s life cycle) to create strategies to sustain their product’s longevity or change it to meet market demand or adapt with/to developing technologies.
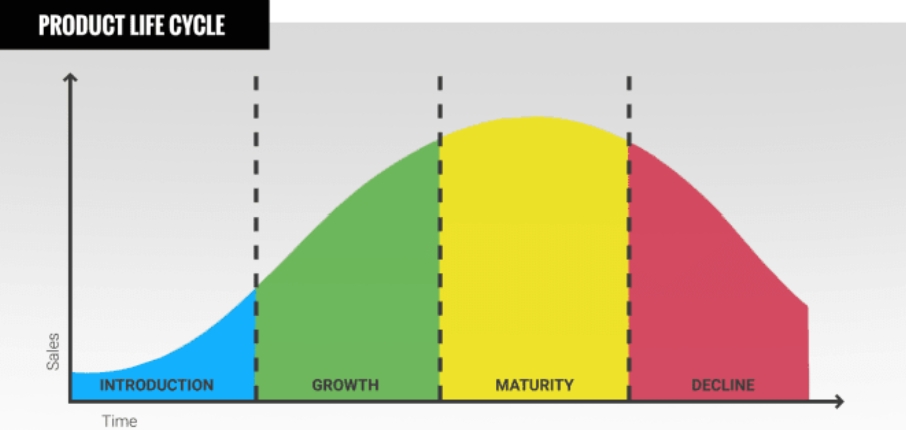
The Different stages of Product life Cycle:-
A) Introduction: This is the stage when a product is launched, and it involves high investment and lower profits. Companies focus on inducing acceptance and increasing awareness.
B) Growth: In this stage, the product shows better returns on investment, but competition intensifies. Companies may introduce secondary products or support services.
C) Maturity: At this stage, competition and duplication become challenges. Penetration pricing by competitors can affect the product’s unique selling points. Sales revenue remains high, but growth potential decreases.
D) Decline: This is the final stage where sales and profits decline, and a product may exit the market. Companies become cost-conscious and may allocate resources to different projects.
The marketing strategies at each stage:
1. Introduction:
– Goal: Create awareness and attract early customers.
– Strategy: Heavy advertising, highlight product features, limited distribution.
– Pricing: Often set at a premium.
2. Growth:
– Goal: Expand market share and maximize profits
– Strategy: More advertising, expand distribution, possibly introduce variations.
– Pricing: Stable or slightly reduced.
3. Maturity:
– Goal: Maintain market share, focus on differentiation.
– Strategy: Emphasize brand, product diversification, cost control.
– Pricing: Competitive, potential discounts.
4. Decline:
– Goal: Manage declining sales or exit the market.
– Strategy: Cut costs, focus on niche markets, discontinue if needed.
– Pricing: May decrease to clear inventory.
Or
Strategies for the differing stages of the Product Life Cycle
A) Introduction: The need for immediate profit is not a pressure. The product is promoted to create awareness. If the product has no or few competitors, a skimming price strategy is employed. Limited numbers of product are available in few channels of distribution.
B) Growth: Competitors are attracted into t okhe market with very similar offerings. Products become more profitable and companies form alliances, joint ventures and take each other over. Advertising spend is high and focuses upon building brand. Market share tends to stabilise.
C) Maturity: Those products that survive the earlier stages tend to spend longest in this phase. Sales grow at a decreasing rate and then stabilise. Producers attempt to differentiate products and brands are key to this. Price wars and intense competition occur. At this point the market reaches saturation. Producers begin to leave the market due to poor margins. Promotion becomes more widespread and uses a greater variety of media.
D) Decline: At this point there is a downturn in the market. For example more innovative products are introduced or consumer tastes have changed. There is intense price-cutting and many more products are withdrawn from the market. Profits can be improved by reducing marketing spend and cost cutting.
4. What is Packaging? Explain its role and functions. Mention it features, advantage of Packaging 2015, 2018,2022
ANSWER – Packaging is the science, art, and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. It plays a crucial role in marketing, protecting the product, and ensuring its safe and efficient delivery to consumers.
Role of Packaging:
1. Protection: Packaging shields products from external factors like moisture, light, air, and physical damage, ensuring their integrity and quality.
2. Containment: It holds the product securely, preventing spillage or breakage during transportation and handling.
3. Information: Packaging provides essential information to consumers, including product details, usage instructions, and safety warnings.
4. Marketing and Branding: It serves as a powerful marketing tool, conveying the brand’s identity and influencing consumer purchasing decisions.
5. Convenience: Packaging can be designed for ease of use and storage, enhancing the overall consumer experience.
Functions of Packaging:
1. Containment: The primary function of packaging is to hold and protect the product.
2. Protection: It safeguards the product from environmental factors and damage.
3. Information: Packaging conveys vital product information and instructions.
4. Marketing: Packaging serves as a marketing tool, attracting consumers and conveying brand identity.
5. Convenience: Packaging can make it easy for consumers to use and store the product.
Features of Effective Packaging:
– Durability: Packaging should be sturdy to protect the product during transit.
– Visual Appeal: Eye-catching design and graphics can attract consumers.
– Sustainability: Environmentally friendly packaging is a growing trend.
– Size and Shape: Packaging should fit the product’s size and shape.
– Information: Clear and accurate product information is essential.
– Tamper Resistance: Packaging can deter tampering and ensure product safety.
– Cost-Efficiency: Packaging should be cost-effective for both production and transportation.
Advantages of Packaging:
1. Protection: It safeguards the product from damage, spoilage, and contamination.
2. Branding: Packaging is a powerful tool for brand recognition and marketing.
3. Information: It provides consumers with crucial information about the product.
4. Convenience: Packaging can make products easy to use and store.
5. Differentiation: Unique and attractive packaging can set a product apart in a competitive market.
6. Sustainability: Eco-friendly packaging options reduce environmental impact.
5. What is brand name and trade mark? Explain their relative merits and demerits.2022
ANSWER – Certainly, here’s the explanation without any stars or bold text:
A brand name and a trademark are related but distinct concepts, both essential for protecting and promoting a company’s identity and products. Here’s an explanation of each and their relative merits and demerits:
Brand Name:
– A brand name is the unique name given to a product or service to identify it and distinguish it from others in the market.
– It’s part of a brand’s identity and plays a crucial role in brand recognition and customer loyalty.
Merits of Brand Names:
1. Recognition: A well-chosen brand name can enhance recognition among consumers.
2. Customer Loyalty: A strong brand name can build trust and loyalty.
3. Differentiation: It helps differentiate products in a crowded market.
4. Cost: Developing and promoting a brand name can be cost-effective.
Demerits of Brand Names:
1. Limited Legal Protection: Brand names may not have the legal protection that trademarks offer.
2. Potential Confusion: Similar brand names in the market can lead to consumer confusion.
Merits of Trademarks:
1. Legal Protection: Trademarks offer legal protection against infringement, providing exclusive rights to use the mark.
2. Asset Value: Trademarks can have significant asset value and can be bought, sold, or licensed.
3. Global Reach: Trademarks can be registered internationally, offering protection in various markets.
Demerits of Trademarks:
1. Legal Costs: Registering and protecting trademarks can involve legal fees.
2. Complex Process: The trademark registration process can be complex and time-consuming.
3. Renewal and Maintenance: Trademarks need to be renewed periodically, and maintenance is required to ensure continued protection.
Trademark:
– A trademark is a legally registered symbol, word, or combination that uniquely identifies and protects a company’s products or services.
– It provides legal protection against unauthorized use by competitors and helps safeguard the brand’s identity.
– Merits:
– Legal Protection: Trademarks offer legal protection against infringement, providing exclusive rights to use the mark.
– Asset Value: Trademarks can have significant asset value and can be bought, sold, or licensed.
– Global Reach: Trademarks can be registered internationally, offering protection in various markets.
– Demerits:
– Legal Costs: Registering and protecting trademarks can involve legal fees.
– Complex Process: The trademark registration process can be complex and time-consuming.
– Renewal and Maintenance: Trademarks need to be renewed periodically, and maintenance is required to ensure continued protection.
6. Describe in brief the various components of Product planning. Distinguish between product standardization and product simplification. 2017
ANSWER – Product Planning Components:
Product planning involves several key components to ensure the successful development and launch of a product. These components typically include:
1. Market Research: Gathering data on customer needs, preferences, and market trends to identify opportunities.
2. Idea Generation: Generating product ideas based on market research, consumer feedback, and internal creativity.
3. Idea Screening: Evaluating and filtering product ideas to focus on those with the most potential.
4. Concept Development and Testing: Developing product concepts and testing them with target consumers to assess interest and viability.
5. Business Analysis: Conducting a detailed analysis of the product’s potential financial aspects, including cost, pricing, and revenue projections.
6. Product Development: Turning the chosen concept into a tangible product, involving design, engineering, and prototyping.
7. Market Testing: Introducing the product to a limited market to gather real-world feedback and identify any issues before a full-scale launch.
8. Commercialization: Preparing for the full-scale launch, including marketing, distribution, and sales strategies.
9. Launch: Introducing the product to the broader market and customers.
Distinguish between product standardization and product
simplification:-
| Aspect | Product Simplification | Product Simplification |
| Definition | Making a product uniform and consistent with little variation to serve a wide, global market. | Reducing complexity and features in a product to make it more straightforward and user-friendly. |
| Purpose | Reduce production costs, streamline manufacturing processes, ensure consisten | Improve usability, reduce production costs, target specific market segments. |
| Examples | Standardizing products like smartphones, fast food items, or industrial components for global markets. | Simplifying user interfaces in software for less tech-savvy users, or simplifying ingredients in food products for health-conscious consumers. |
| Merits | Cost efficiency, consistent quality, easier global market entry. | Enhanced usability, reduced costs, targeted marketing. |
| Demerits | Limited customization, potential market insensitivity to local preferences | Reduced feature set, potential loss of appeal to advanced users. |

